Customer data integration: How businesses generate data today
To understand the role CRM integration plays in customer data integration, let’s first zoom out and gain insight into how modern businesses operate.
Every business process generates loads of data about its customers. This includes their:
- Channel preferences
- Product preferences
- Previous purchases
- Privacy preferences
- Loyalty rewards
- Persona details

This data is sourced from sales channels (e.g., POS), marketing platforms, in-store branches, and financial dashboards, among other channels.
It plays a role in helping your business create the best products, for the right customers, at the most profitable price point relative to your competitors.
Trying to run a business without unifying this data leads to disorganized processes, flawed business decisions, unhappy customers, and an impacted bottom line.
Here are just a few examples of how this plays out:
- Customer support: Not unifying customer support ticket details leads to delayed resolutions, unsatisfied customers, and low reviews. Such chaos may come from having to deal with multiple sources of customer data: customer contact details are in CRM while order histories are in SAP, purchase details are in a POS system, and customer support tickets are in Zendesk.
- Inventory: Not updating inventory levels leads to oversold stock, late or failed deliveries, unhappy customers, and potential chargeback fees.
- Marketing: With customer contact details spread out across different databases, marketers end up creating ineffective or poorly targeted marketing campaigns, leading to weak results and wasted resources.
- Forecasting: When customer payments aren’t updated across the board, this leads to sales forecasts and quotas based on incomplete, inaccurate, or outdated financial data.
- Communications: When new reps can’t see old customer support emails to existing clients, they end up repeating troubleshooting questions and delaying progress due to lack of context.

To overcome these challenges, businesses must organize all their customer data into a single, coherent customer view housed in the right data integration tool.
Let’s now explore:
- What a customer view is
- How businesses currently handle customer data integration
- What data integration solution they should use, and
- Best practices to follow for effective data integration
Defining the customer view
A 360-degree customer view is a complete, timely, and accurate view of a business’s customers.
Such a complete view gives the company’s stakeholders – its employees, partners, directors, and investors – the insight they need to make effective decisions.
Without a 360-degree customer view, you get:
- Marketing building campaigns without accurate sales data
- Sales selling without insight into customer support complaints
- Customer support failing to live up to promises made by marketing and sales
With a 360-degree customer view, each department gets full access to customer data, meaning that:
- Marketing can see which customers buy the most and craft campaigns around those segments
- Sales can address the most common complaints and overcome sales objections more effectively
- Customer support can resolve issues faster and find more profitable product or delivery gaps to fill

A 360-degree customer view isn’t just about collecting data. It’s about unifying it in a coherent manner to improve the customer experience at all levels. So, how are business managers currently going about this task?
How businesses handle customer data management today
Businesses currently try to integrate their data in three main ways:
- Custom code: With this approach, companies pay developers and integration specialists to write code that collects and standardizes data across different sources. Data integration through custom code is expensive, time-consuming, and neither scalable nor easy to maintain. If one data source changes, for example, you have to update the code that links that source to your database.
- Manually: Staff members collect, organize, and present data from disparate sources in one place. Think updating sales orders in Excel every day, or trawling through emails to find invoices and update payment data.
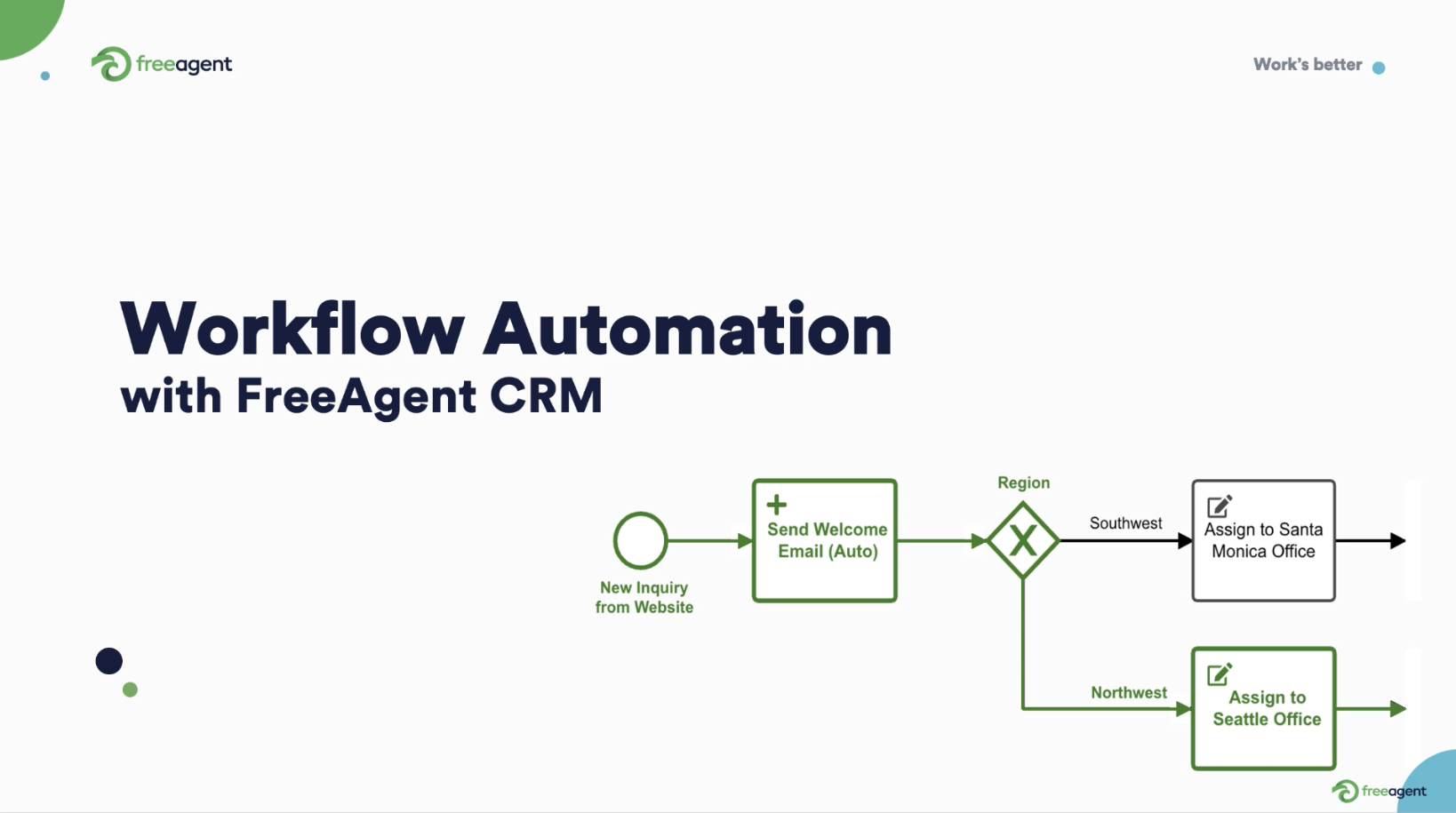
- APIs: APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) allow software tools to talk to each other in a common language. Using APIs, software tools automatically pull and update data as needed. Think of the API approach as a hub and spoke model, with your data repository in the middle pulling data from each source through APIs.

Tools that help businesses achieve a 360-degree customer view
Customer data integration forms part of any business’s digital transformation strategy. There are different tools you can use to consolidate customer data: Spreadsheets, ERP tools, BI tools, and CRM software.
- Spreadsheets are familiar to most people, but you need manual intervention and technical know-how to integrate them with other tools.
You may also have to deal with multiple spreadsheets for different types of data, without an easy way to integrate them all or ensure data quality.
This makes spreadsheets the least practical tool for effective customer data integration.
- ERP software can handle complex customer data management needs, but ERP software is often overkill for small businesses that need a simple tool to manage their data. Due to its cost and complexity, it may also take longer to master ERP software and use it as an effective customer data platform.
- Business intelligence (BI) tools collect data from different sources into complex dashboards you can use to make business decisions around the customer journey.
If big data is all you need, business intelligence tools are an excellent customer data platform choice.
However, you can’t simultaneously run your sales and marketing operations using BI tools (e.g., creating quotes or storing customer contact data). You’re forced to export that data to your CRM, ERP, or other sales tool for action.
This makes BI software a useful customer data silo but an ultimately impractical customer service platform.
- A CRM is an affordable, secure, and easy-to-use data consolidation tool. It unifies your customer data, helping you see everything at a glance, make the right decisions around your ideal customer profile, and generate actionable insights.
Few software tools put customer information in one place – and allow you to execute on it – like modern CRM software.

The best CRMs come with API access, which unlocks and transfers customer data flexibly across different apps. This frees you up from manual updating or expensive custom coding.
With a choice between spreadsheets, ERP tools, BI software, and CRM platforms, CRM is the best choice for small businesses looking to consolidate their data at an affordable price.
Best practices: 4 steps for effective customer data integration
How should companies kick off their customer data integration efforts following best practices? There are 4 key steps to this process:
- Assess your data sources
- Get the right tools
- Gather the right team
- Execute the integration plan

1. Assess your data sources
The first step is to assess your data sources by asking the following questions:
- What type of customer data does our business gather? This could be contact data, sales order histories, communication preferences, location data, and demographic data.
- What channels and sources currently feed that data in? This could be financial dashboards, social media platforms, marketing automation platforms, ad platforms, customer support platforms, and productivity tools like calendars and email apps.
- How often do those sources need to be monitored for accuracy? For instance, financials might require daily monitoring while social media analytics need weekly reporting.
- What formats do these data pieces come in – and are they standardized? For example, name fields might be depicted as first-middle-last in one system, while only stored as firstname-lastname in another. Similarly, a customer’s ID document may be stored as a JPEG in one system while rendered as a PDF in another. Best practices suggest standardizing your data formats.
- What resources do you allocate to managing that data inflow currently? For instance, do you have a full time accountant managing the financials? Are your social media analytics reported in-house or through an agency?
- Can these sources be automated to reduce extra work? For example, instead of recording sales data manually, could you switch to an order management system that automatically records and reports new sales? Could you phase out manual social media reporting in favor of automated monthly reports?

2. Get the right tools
Data must be stored and managed properly for it to be used effectively. To do this, you’ll need a central database where all of this data sits, such as an on-premise ERP system, spreadsheets, cloud-based CRM platform, or a BI tool.
This central repository will also need to be actively managed. This can involve hiring a dedicated CRM administrator, performing ongoing CRM hygiene, and doing CRM training to teach staff how to use it.
3. Gather the right team
Many CRM implementations fail due to inertia and lack of organizational buy-in. It’s crucial to align together who feeds data into the business, and this could be the:
- Sales leader that works with sales data
- Marketing leader who manages marketing data
- Management team that handles resource allocation
As you bring everyone together on this journey, explain the rationale, indicate the required data and formats, and assign a lead for your CRM integration project. A project lead ensures there’s clear accountability and leadership during the initiative.
4. Execute the integration plan
With your data tally, integration team, and desired tool(s) in place, it’s time to link up your existing data sources to your CRM software through APIs.
Your CRM’s support specialists or implementation specialists can help with this step. For best results, transfer data in batches and monitor the process for data migration errors.
Next, test your CRM integration by pulling in data from different sources to check its accuracy.
Finally, revisit your data connections often to ensure the right data is being fed into your CRM.
Choose FreeAgent CRM for customer data integration
The right CRM can ease your customer data integration efforts, and FreeAgent CRM is built to manage that process.
FreeAgent emphasizes the account view – allowing you to see who you’re talking to, what products they’ve bought (and for how much), what company they’re from, what emails they’ve sent, and what their lead score is – all in one view.
In other words, it’s a customer data hub that handles data collection and gives you actionable insights into customer behavior to help you improve the customer experience.
FreeAgent’s API access means you can connect your emails, sales data, and accounting records into one platform, accessible by your team. Access-based controls mean you can control exactly who gets to see what, granularly.
This holistic view lends context to every contact in your database, allowing you to make better business decisions, faster.
Try FreeAgent CRM today and take your customer data integration efforts to the next level.